Comparison
ADVANCED ELECTROCHEMICAL HYBRID TECHNOLOGY
Compared with Biological Methods
| FEATURE | ELECTROCHEMISTRY | BIOLOGICAL |
|---|---|---|
| Footsteps | Simple installation & low footprint | Requires a wide footprint |
| Required area | 300 M² AREA FOR 1000 KLD | 1200 M² AREA FOR 1000 KLD |
| Civilian employment requirements | Little civil power | More civilian power |
| Human power | Requires less human labor | It requires a lot of human power |
| Storage tank requirements | Fewer number of storage tanks | More number of storage tanks |
| Civil costs | Low civil costs | Civil costs are high |
| Equipment costs | Equipment costs are marginally higher | Low equipment costs |
| Operating costs | Low operating costs | High operating costs |
| Terminal care | Better terminal care | Terminal care is poor |
| Oil and fat | Removes oil and grease | Requires oil and grease filter |
| Heavy metal | Removes heavy metals | Heavy metals cause bacteria |
| Complex & stubborn organic | Removes complex & stubborn organics | Less efficient in removing stubborn organics |
| Disinfection | Destroys & removes bacteria, cysts & viruses | Requires additional disinfection to remove bacteria, cysts & viruses |
| Toxicity | Resists toxicity | Cannot tolerate toxicity |
| Washing waste | Waste in washing care | Requires separate washing treatment |
| Nutrition | Eliminates nutrients | Nutrient removal requires extensive additional unit operations |
| Precipitate | More stable deposits | Unstable deposits |
| Storage life | The storage life of treated water is better | The storage life of treated water is shorter |
| External chemistry | Does not require external chemicals for disinfection | Requires external chemistry for disinfection |
| Consistency | Consistent and reliable | Consistency is low and requires monitoring |
| Moving components | Few moving parts | Lots of moving parts |
| Process | Few units are in process | Many units are in process |
| Chemistry | Chemical free | Requires some chemicals |
| MLSS | Does not require MLSS maintenance | Requires MLSS maintenance |
| pH Treatment | Does not require pH treatment | Requires pH maintenance |
| Temperature | Free temperature | Depends on temperature |
| Start and Stop | Start and stop at will | Need to keep running |
| Start up time | Accelerated start up | Slow start up process |
| Toxicity resistance | Resistant to toxicity | Not resistant to toxicity |
| Bacterial needs | The process does not involve bacteria | It needs to revive the bacteria if inactivation occurs and takes time |
| Cleaning and replacement | Periodic cleaning and replacement of electrodes is necessary | Regular cleaning and replacement of diffusers will be necessary |
| Operation and maintenance | Easy to operate and low in maintenance | Not easy to operate and maintain |
| Greenhouse Gas Yield | Produces less Greenhouse Gases | Produces more Greenhouse Gases |
| Atmospheric oxygen | Does not reduce atmospheric oxygen | Reducing atmospheric oxygen (250 Kg/MLD) = (4,000 Trees, 20 Hectares of Land/MLD) |
| Oxygen in flow | Does not reduce oxygen in the flow | Reduces oxygen in the flow |
| Eutrophication flow | Does not cause eutrophication flow. Removes nutrients better | Causes eutrophication flow |
| Resource conservation | Significant conservation of valuable resources | Lack of conservation of water resources |
| Chemical use/preservation | Save on chemicals | Use of chemicals |
| Sludge processing | Single component in processing sediment | Multi components in processing sediment |
| Smell | Odor free air | The air is not odor free |
| Noise | Noiseless operation | Makes noise |
PROFIT
USE OF OUR PRODUCTS
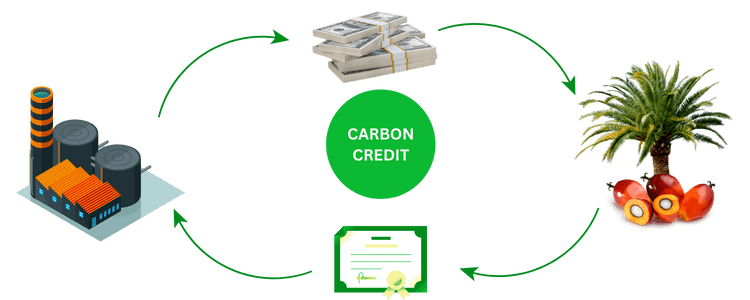
CARBON CREDIT
Carbon credits are tradable permits or certificates that give holders the right to produce one tonne of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gas equivalents.
The main goal of creating carbon credits is to reduce emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases.
Companies that achieve carbon offsets (reducing greenhouse gas emissions) will be given additional carbon credits.
PROFIT
USE OF OUR PRODUCTS

GREEN BOND
Green Bonds or green bonds, known as Environmentally Friendly Bonds, are an instrument in seeking financing only for environmentally friendly projects.
Green Bond project financing is aimed at efficient energy use, pollution prevention, sustainable agriculture, fisheries and forestry, as well as clean water and sustainable water management.
Green Bond Certified